- For U.S. Residents Only
- IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
- Full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
- Contact Us


Enoxaparin Sodium Injection is an anticoagulant, also known as a blood thinner, that slows the body’s normal clotting process—reducing your risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Since you may still be at risk for developing DVT blood clots even after leaving the hospital, continuing enoxaparin treatment at home is an important step in reducing your risk of developing DVT blood clots. This website provides instructions on how to administer Enoxaparin Sodium Injection at home.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
If you are receiving epidural or spinal anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture, and taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, you may be at increased risk of developing a blood clot in or around the spine, which can result in long-term paralysis. Your risk may be further increased if you:
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors (such as aspirin), or other anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Have an indwelling epidural catheter
- Have a history of spinal trauma, or repeated spinal anesthesia or punctures
- Have a history of spinal deformities or spinal surgery
It is important to contact your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms such as tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), or muscular weakness.
Please see additional Important Safety Information »
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
The information presented here does not take the place of injection instructions you may have received from your health care provider.
Watch How to Use Enoxaparin Sodium Injection Prefilled Syringe
NDC & Wholesaler Numbers+/-
| Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, USP Prefilled Syringes* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Description |
Product Number |
Unit of Sale NDC |
Wholesaler Numbers | |||
| ABC | Cardinal | McKesson | Morris & Dickson |
|||
| 30 mg per 0.3 mL | 551993 | 63323-559-93 | 10230848 | 5576020 | 2460921 | 789727 |
| 40 mg per 0.4 mL | 556497 | 63323-564-97 | 10230861 | 5576038 | 2461903 | 789735 |
| 60 mg per 0.6 mL | 556698 | 63323-566-98 | 10230832 | 5576046 | 2460913 | 789792 |
| 80 mg per 0.8 mL | 558499 | 63323-584-99 | 10230862 | 5576053 | 2460905 | 789800 |
| 100 mg per 1 mL | 558696 | 63323-586-96 | 10230835 | 5576061 | 2459089 | 789818 |
| 120 mg per 0.8 mL | 556099 | 63323-655-99 | 10230827 | 5576079 | 2460970 | 789826 |
| 150 mg per 1 mL | 558994 | 63323-589-94 | 10230779 | 5576087 | 2460947 | 789834 |
Indications & Usage+/-
Indications & Usage
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE) in patients:
- Undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk of thromboembolic complications
- Undergoing hip-replacement surgery, during and following hospitalization
- Undergoing knee-replacement surgery
- At risk for thromboembolic complications due to severely restricted mobility during acute illness
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection is indicated for treatment of acute DVT:
- The INPATIENT TREATMENT of acute DVT, with or without PE, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium
- The OUTPATIENT TREATMENT of acute DVT, without PE, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection is indicated for the prophylaxis of ischemic complications of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, when concurrently administered with aspirin.
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, when administered concurrently with aspirin, has been shown to reduce the rate of the combined endpoint of recurrent myocardial infarction or death in patients with acute STEMI receiving thrombolysis and being managed medically or with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
The information presented here does not take the place of injection instructions you may have received from your health care provider.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION+/-

Important Safety Information
If you are receiving epidural or spinal anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture, and taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, you may be at increased risk of developing a blood clot in or around the spine, which can result in long-term paralysis. Your risk may be further increased if you:
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, or other anticoagulants, such as aspirin or blood thinners
- Have an indwelling epidural catheter
- Have a history of spinal trauma, or repeated spinal anesthesia or punctures
- Have a history of spinal deformities or spinal surgery
It is important to contact your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms such as tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), or muscular weakness.
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection should not be used in patients who are actively bleeding or who have a low count of blood cells called platelets, which aid in clotting. This is a condition called “thrombocytopenia.” Enoxaparin Sodium Injection also should not be used in patients who are allergic or sensitive to Enoxaparin Sodium Injection or enoxaparin, heparin, or pork products.
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection must be used with care in patients who have any of the following: problems with clotting, uncontrolled high blood pressure, a recent ulcer, impaired vision due to diabetes, kidney problems, and excessive bleeding. Pregnant women with mechanical prosthetic (artificial) heart valves may be at higher risk for blood clots. These patients who are treated with Enoxaparin Sodium Injection must be carefully monitored by their doctor.
Some patients on Enoxaparin Sodium Injection can experience drops in their platelet counts, a condition called “thrombocytopenia.” Also, a serious but rare condition called “heparin-induced thrombocytopenia” can occur with Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. If you have had this condition, you must promptly notify your healthcare professional.
Enoxaparin Sodium Injection alters the blood’s ability to clot. Excessive bleeding (hemorrhage), leading to death, has occurred with Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. Bleeding can occur at any site with Enoxaparin Sodium Injection use. The use of aspirin and other NSAIDs may enhance the risk of excessive bleeding. Be sure to tell all your doctors and dentist about all of the medications you are taking, including those you are taking without a prescription, such as aspirin or other NSAIDs. Also be sure to tell your doctor or dentist you are taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection before any surgery is scheduled and before any new drug is taken.
All patients should be carefully monitored by their doctor while taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. Your doctor is likely to obtain blood tests that measure your blood count and check for signs of hidden bleeding while you are on Enoxaparin Sodium Injection.
You should call your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following: unusual bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, unusual bruising, signs of thrombocytopenia (such as a rash or dark spots under the skin), tingling or numbness (especially in the lower limbs), and muscular weakness.
Before taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, tell your doctor if you have kidney or liver disease, if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or become pregnant while taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, if you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed, about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
The most common side effects from the use of Enoxaparin Sodium Injection are mild pain, irritation, bruising, or redness of the skin at the site of injection. Other common side effects include bleeding, anemia, diarrhea, nausea, ecchymosis, fever, edema, peripheral edema, dyspnea, confusion, and injection site pain.
These are not all the possible side effects of Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. Tell your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Do not stop taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection without first talking to the doctor who prescribed it for you.
For specific questions about your health, you should always consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional who is responsible for your care.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use Enoxaparin Sodium Injection safely and effectively. To learn more about Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Please see full prescribing information for Enoxaparin Sodium Injection, USP, including boxed warning, for additional important information. The full prescribing information is also available at www.fresenius-kabi.com/us.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
DOs AND DON'Ts+/-
The Dos and Don'ts of Continuing Treatment

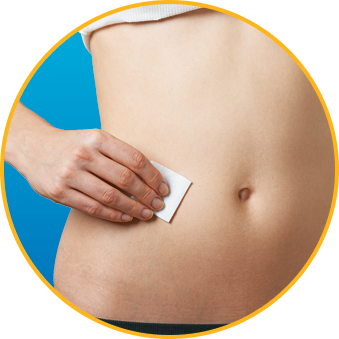
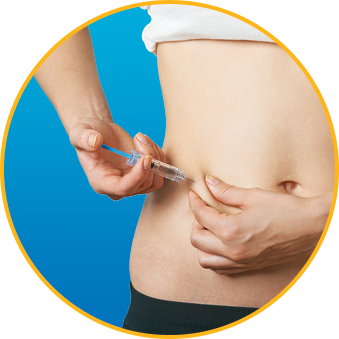
- DO alternate injection site with every injection
- DO administer enoxaparin at the same time every day
- DO look for unusual signs of bleeding
- DO store enoxaparin at room temperature, away from light and moisture
- DO use a new syringe if the safety shield is accidentally activated before use; safely store away the defective syringe and call your pharmacist for more information
- DO tell your doctor about other medications you may be taking, including those that do not require a prescription

- DON’T give enoxaparin to anyone other than the person it was prescribed for
- DON’T take the following medications while taking enoxaparin, unless otherwise instructed by your doctor. They may increase your risk of bleeding:
- - ASPIRIN OR ASPIRIN-CONTAINING PRODUCTS
- - OTHER PLATELET INHIBITORS
- - SALICYLATES (ASPIRIN-LIKE PRODUCTS)
- - NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS), SUCH AS IBUPROFEN, NAPROXEN, OR KETOROLAC
- - COLD OR ALLERGY PRODUCTS, OR PAIN RELIEVERS THAT CONTAIN ANY OF THE ABOVE DRUGS
YOU SHOULD CALL YOUR HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONAL RIGHT AWAY IF YOU NOTICE ANY OF THE FOLLOWING:
- Bleeding or oozing from surgical wound
- Any other bleeding episodes; for example, bleeding at the site of the injection, nosebleeds, blood in your urine, or if you cough or vomit blood
- Spontaneous bruising (a bruise not caused by a blow or any apparent reason)
- Pain or swelling in any part of your leg, foot, or hip
- Dizziness, numbness, or tingling
- Rapid or unusual heartbeat
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Vomiting, nausea, or fever
- Confusion
The information presented here does not take the place of injection instructions you may have received from your health care provider.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
What is DVT?+/-
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
DVT is a condition in which a blood clot, called thrombus, forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, usually in the lower leg or thigh. Most often, a DVT blood clot occurs when blood flow is slowed following surgery, prolonged hospital stays, or extended bed rest due to injury or illness.
If a DVT blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can become lodged there, blocking blood flow and leading to a pulmonary embolism (PE), an extremely serious and potentially fatal condition.
What Increases Your Risk of DVT Blood Clots?
- Advanced age
- Birth control pills, pregnancy, and hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Certain types of cancer and its treatment
- Respiratory failure
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Clotting disorders
- Congestive heart failure (CHF)
- Obesity
- Prior DVT blood clot
- Prolonged immobility
- Surgery (abdominal surgery, knee- or hip-replacement surgery)
What Are the Warning Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)?
As many as half of all DVT blood clots occur without any noticeable symptoms.
Call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following warning signs of a DVT blood clot:
- Swelling, discoloration, or redness in the leg
- Pain or tenderness in the leg
- Warmth over the leg
Call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following warning signs of PE in your lung:
- Chest pain
- Rapid pulse (racing heartbeat)
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Cough, with or without blood
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fever up to 101°F
How Can You Reduce Your Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
The choices you make in your day-to-day activities can go a long way toward reducing your risk of DVT.
- Ask your doctor about blood-flow enhancing exercises
- Check with your doctor before taking any new medications, vitamins, or supplements
- Do not smoke
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Talk to your doctor about any changes in your health
- Try to avoid extended periods of sitting—moving your feet or stretching your legs in a seated position can help
Before starting a new diet or exercise plan, be sure to talk to your doctor.
Important Safety Information for Enoxaparin Sodium Injection
The most common side effects from the use of Enoxaparin Sodium Injection are mild pain, irritation, bruising, or redness of the skin at the site of injection. Other common side effects include bleeding, anemia, diarrhea, nausea, ecchymosis, fever, edema, peripheral edema, dyspnea, confusion, and injection site pain. Please see additional Important Safety Information »
The information presented here does not take the place of injection instructions you may have received from your health care provider.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
FAQs+/-

Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I need to continue Enoxaparin Sodium Injection
treatment at home?
Because of your surgery or medical condition, there is a risk that DVT blood clots can develop after you leave the hospital. Your doctor has prescribed Enoxaparin Sodium Injection for continued therapy at home in order to help protect you against the risk of developing DVT blood clots.
Where should I store Enoxaparin Sodium Injection?
Be sure to store your prefilled syringes at room temperature of 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF), away from light and moisture, and out of the reach of children.
May I inject Enoxaparin Sodium Injection anywhere other than
the abdominal area?
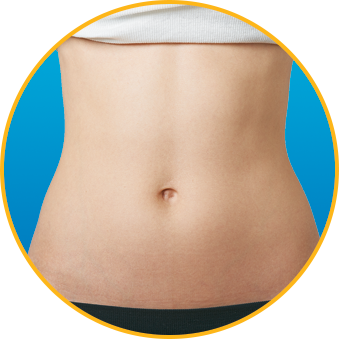
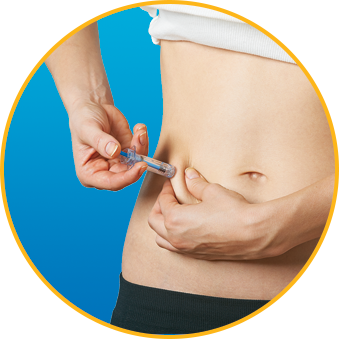
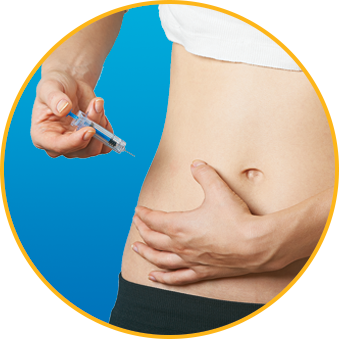
No. Enoxaparin Sodium Injection should be injected into the fatty tissue only, which is why the abdomen is the recommended injection site. It is important not to inject Enoxaparin Sodium Injection into the muscle, as it can cause you to bruise, which can be uncomfortable.
How do I dispose of the used syringes?
Put the used syringe and needle cap in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not dispose of syringes or needle caps in your household trash. If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container.
There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles, syringes, and prefilled syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
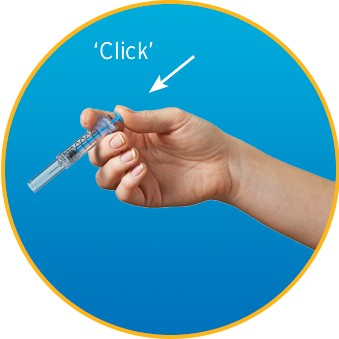
What should I do if the automatic safety device has already been activated?
Do not use the syringe—use a new one for your injection. Keep the defective syringe safely stored and contact your pharmacist for more information.
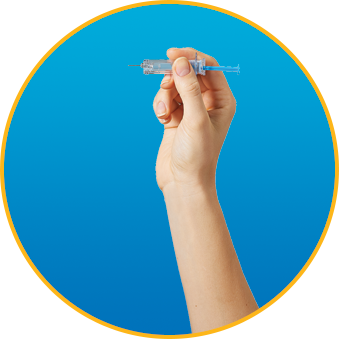
What should I do if there is an air bubble in the syringe?
Every syringe comes with a small air bubble. DO NOT expel the air bubble unless your doctor instructs you to adjust your dose. It’s safe to give yourself the injection, even with the air bubble.
What should I do if I think I have given myself too much Enoxaparin Sodium Injection?
Call your health care provider immediately, even if you don’t see or feel any unusual symptoms right away.
My doctor has prescribed less than a full syringe for me. What should I do?
Hold the syringe with the needle pointing down, but close enough so you can read the writing. Then expel the excess portion, and tap it off until the contents align with the dosage that your physician prescribed.
Who should I call if I have more questions about Enoxaparin Sodium Injection?
For specific questions about your Enoxaparin Sodium Injection treatment, consult your doctor or a qualified health care professional who is responsible for your care.
If you have questions regarding the Enoxaparin Sodium Injection Kit, please call Fresenius Kabi at (800) 551-7176.
How do I learn more about the risks of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) blood clots and treatment with Enoxaparin Sodium Injection?
To find out more about what increases your risk for developing DVT blood clots and how Enoxaparin Sodium Injection anticoagulant therapy works to help reduce these risks, talk to your doctor.
Important Safety Information for Enoxaparin Sodium Injection
All patients should be carefully monitored by their doctor while taking Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. Your doctor is likely to obtain blood tests that measure your blood count and check for signs of hidden bleeding while you are on Enoxaparin Sodium Injection. Please see additional Important Safety Information »
The information presented here does not take the place of injection instructions you may have received from your health care provider.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
Contact Us
Full Prescribing Information including Boxed WARNING »
HCP Training Requests
Contact Clinical-Nurse-Liaisons@Fresenius-Kabi.com to request training for your healthcare profesional.
Order Discharge Kit
Discharge kits may only be ordered by healthcare professionals.
The Discharge Kit Contains:
- Sharps Disposal Container
- Alcohol Swabs
- Booklet